NIH/NLM rolls out an updated PubMed
An updated version of PubMed will replace the current version; the new PubMed is currently scheduled to become the default in spring 2020, replacing the legacy version. According to the November-December 2019 NLM Technical Bulletin, new features include:
Improved search
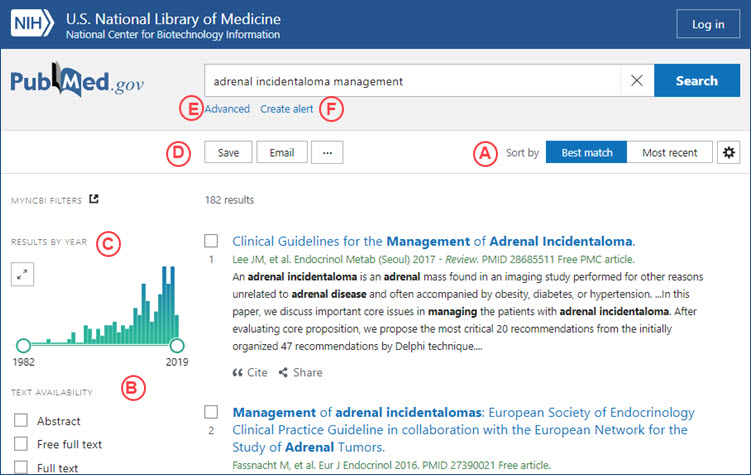
Find highly relevant articles more easily using the Best Match sort (see A below), now the default sort order in PubMed. Best Match uses a state-of-the-art machine learning algorithm that is trained on aggregated user searches. The Best Match algorithm ranks search results according to several relevance signals. For more information about Best Match, please see the article, Best Match: New relevance search for PubMed.
The features and data you rely on
The new PubMed includes the features you rely on for searching, as well as saving and sharing your results.
- Access the same trusted database of more than 30 million citations for biomedical literature.
- Activate the default filters or customize the filter menu to meet your needs (see B below).
- Use the Results by Year graph to see trends in literature over time or to refine your search results by publication year (see C below).
- Save your search results to a file, email your results to yourself or a colleague, or send your results to a clipboard, collection, or your NCBI My Bibliography (see D below).
- Go to the advanced search page to search for terms in a specific field, see the search details, review your search history and combine searches to create complex search strings (see E below).
- Save your search and create an email alert (see F below).
 Responsive Design
Responsive Design
The updated PubMed features a mobile-first, responsive layout that offers better support for accessing PubMed content with the increasingly popular small-screen devices such as mobile phones and tablets. The interface is compatible with any screen size, which provides a fresh, consistent look and feel throughout the application, no matter how you access it.
Updated Technology
The updated version of PubMed uses Solr, an open-source enterprise search system, for document indexing, and MongoDB for storage and retrieval. In addition to its scalability and reliability, Solr also provides many powerful out-of-the-box search functionalities, such as wildcards, groupings, and joins. For example, unlike the current production PubMed, the updated version does not limit the number of variants for wildcards. The MongoDB storage solution provides default data replication between different data centers, which ensures redundancy. The updated PubMed runs on a modern cloud architecture that provides scalability and a reliable backup environment.
User-Driven Development
The updated PubMed continues to be validated by prioritizing and aligning features based on user research including usability testing and continuous feedback from users.
NIH/NLM staff are iteratively adding functions and improving the system.
___________________________________
Note: The new PubMed interface no longer includes the “Send to Order” feature that connected to multi-item Request. The UC-eLinks button will be present on all full view articles, and will always have a link to Request to place an ILL request for any article.